1.Introduction
1.1 Autonomous Underwater Vehicle(AUV)
AUV (Autonomous Underwater Vehicle), one of the main categories of underwater vehicles, which integrates controllers, sensors, computer software and power, has autonomous perception and intelligent decision-making capabilities, and navigates with its own power. With the ability of autonomous navigation and sailing, it can conduct large-scale navigation and detection missions, and is often used in marine aerial surveying, target search and marine exploration.
The competition tests perception and intelligent control of the AUV (Autonomous Underwater Vehicle) by examining its completion of various underwater tasks. The tasks of competition include: passing the qualification gate, hitting floating ball , underwater precise work and rising onto the flotation frame by tracing acoustics signals. Underwater navigation markers with QR codes will help and guide the AUV during the first 3 tasks; the light beacon or a 37.5kHz acoustic beacon will guide the AUV in the final task.
1.2 Venue&Site
Site Size: length not less than 20m, width not less than 8m, depth from 1.3m to 2.2m.
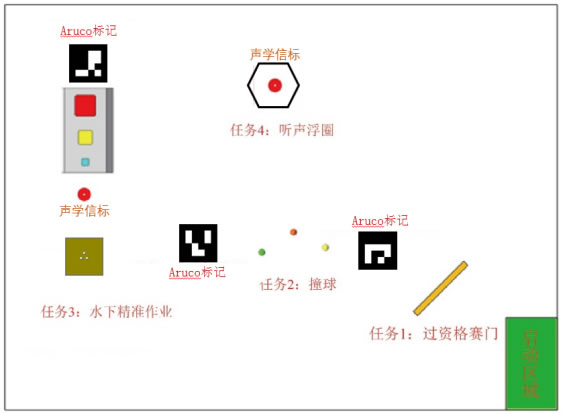
Figure 1 Competition Site Diagram
1.3 Requirements on AUV
1.3.1 Size and Weight
The vehicle must fit into a cube size of 1000mm*1000mm*2000mm. Vehicles weighing 45 kg or more are not allowed to compete.
The team can use 2 vehicles if their total mass and dimensions do not exceed the specified limits.
1.3.2 Power Supply
The power supply can only be rechargeable battery, with the voltage not exceeding 72V. It is forbidden to use a 220V AC power supply.
1.3.3 Emergency Switch
Each vehicle must have a reliable security (emergency) switch to shut down the system and stop all propellers during an emergency. The switch should be placed in a prominent position on the surface of the vehicle, which can be easily operated by the diver in case of emergency.
1.3.4 Others
A.During the competition, except the balls for competition, no parts or accessories can be separated from the vehicle and nothing can be thrown into the pool. There should also be no leakage of oil or other pollution.
B.During the competition, once the AUV (or one of the AUVs) floats onto the surface, the attempt ends. During the competition, no part of the robot shall be above the water except for the floating ring. Once any part floats onto the water, the attempts ends (according to 2.5 End of Competition). That is, during the competition, the robot can only surface once to complete the task of Rising onto the Flotation Frame.
C.The AUVs must autonomously pass all tests. Teams are prohibited from touching the water in pool with any device or using any wireless device to remotely control the vehicles.
D.Total attempt time for each team is 30 minutes, 10 minutes for debugging preparation and 20 minutes for competition. The AUV should pass the gate within 10 minutes after the starting of the race. The attempt ends when any part of the robot floats onto the surface (except Rising onto the Flotation Frame task).
E.If the participants consider that the result of the first attempt is unsatisfactory, then a second attempt may be made. When the team members announce the termination of the attempt, the 20-minute timer is suspended, and the score gained this time is invalid. The staff will salvage the robot and when it is handed over to the team members.
F.A captain for each team can be appointed to contact the judge, participate in the draw and stop the attempt, if necessary.
G.Only if all the four tasks have been completed with scores at the end of the competition, additional points can be awarded for the remaining time the 20-minute timer continues.
2.Competition Tasks
2.1 Passing the Qualification Gate
2.1.1 Props Description
The qualification gate is a rectangular frame made of red PVC pipes, the inner frame size is of 2500mm x 1500mm. The specific dimensions are shown below:
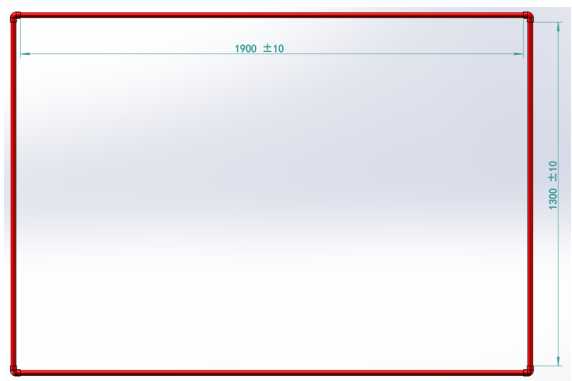
Figure 2 Qualification Gate
Behind the gate, there is a plate with a Aruco code for the positioning and guiding (as shown below). The size of the plate is 400mmx400mm. All Aruco codes are different. The rotation angle (from -180 to 180 degrees) is encrypted in the Aruco code to guide the AUV to the second task.

Figure 3 Aruco code for Positioning and Guiding

Figure 4 Layout and location of Aruco code
2.1.2 Instruction of Rules
The AUV completes the dive in the starting area and begins the tasks, passing through the qualifying gate first and scoring. No points will be awarded for failure to pass the qualifying gate.
Here is the formula to calculate the score of passing the gate:scores = base points + additional points. Passing the gate underwater, the vehicle can get both base points and qualification of attending the subsequent tasks of the game.
Additional points of skilled passing are given for rotating 2 circles in the same direction while passing the door, including horizontal rotation (z axis) and roll rotation (x or y axis). Certain points are awarded for each 90° rotation, but are also deducted for reverse rotation. Full marks are awarded for 2 circles.
Note: Horizontal rotation (z axis) : 5 points each 90°, full score is 40 points.
Roll rotation (x or y axis): 10 points each 90°, full score is 80 points.
2.2 Hitting Floating Ball
2.2.1 Props Description
Three floating balls of different colors will be placed in the pool, each tied to a line with the other end fixed to the bottom of the pool by a heavy object. The distance between the floating balls and the water surface is 0.6m~1.2m, and the height of the floating balls are different, as shown below:
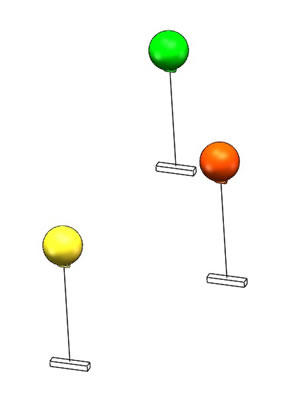
Figure 5. Schematic Diagram of Floating Ball
3 standard inflatable floats with a diameter of 20 cm are used as floating balls. Balls with the help of a rope and a load, are installed in the water at different depths. The horizontal distance between the centers of the floats is about 2m.
2.2.2 Instruction of Rules
The vehicle needs to hit the floats in the water in order which were drawn before taking the competition to score points. If the vehicle doesn’t hit the floats in order, only a lower score can be awarded.
The Aruco marker after the Hitting Floating Ball task indicates the direction of the next task. The size of the Aruco code is 400mm*400mm, and the guide angle is from -180 degrees to 180 degrees.
Figure 6 Aruco Code for Underwater Precision Operation
2.3 Underwater Precise Work
2.3.1 Props Description
A display basket will be installed at the bottom of the pool. Negative buoyance exists in water. Three white balls are placed in the display basket. The dimensions are shown in the following figure:
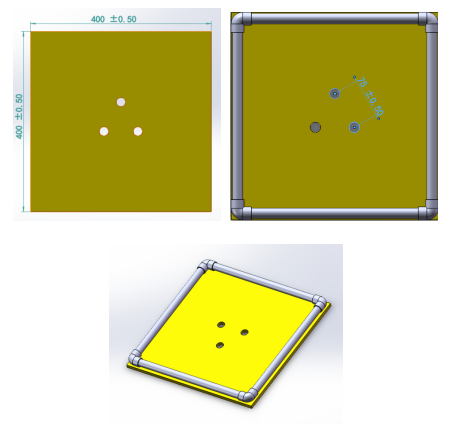
Figure 7 Underwater Golf Display Basket
A storage basket with three cells of different sizes will also be installed next to the frame at the bottom. The vehicle needs to grab the golf balls from the display basket at the bottom and put it into basket cells, as shown below:
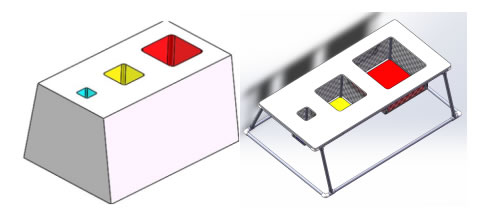
Figure 8 Storage Basket Cells
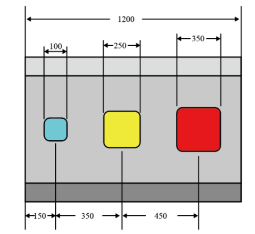
Figure 9 Schematic Diagram of the Storage Basket Size (mm)
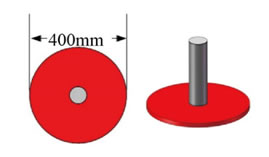
Figure 10 Underwater 30K Acoustic Beacon
The underwater precision operation area is equipped with 30k CW acoustic beacon to help the vehicle locate itself in the area.

Figure 11 Aruco Code for Underwater Precision Operation
A Aruco code is also equipped in the area, to be used to help the vehicle locate itself. Specific Aruco marker need to be further determined.
2.3.2 Instruction of Rules
Besides one yellow golf ball carried by the vehicle, extra balls (white) can be caught from the display basket and cast into the basket cells.
The vehicle can get scores by casting balls in any cells of the basket. The smaller the cell is, the more points the vehicle can get.
2.4 Rising onto the Flotation Frame
2.4.1 Props Description
The floating frame is a regular octagon made up of eight PVC pipes of about 620mm in length.
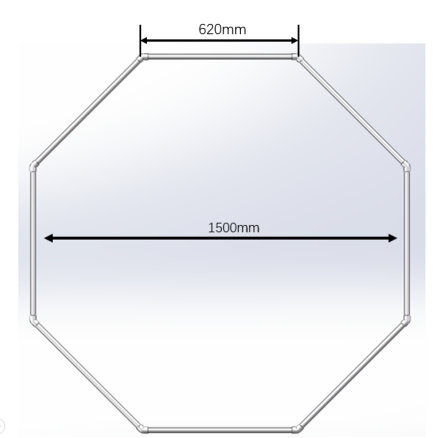
Figure 12 The Floating Frame Diagram
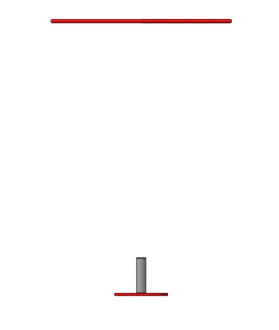
Figure 13 Schematic Diagram of Props for Rising through Floating Frame Guided by Acoustic Beacon
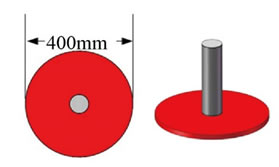
Figure 14 37.5k CW Signal Acoustic Beacon
A 37.5k CW signal acoustic beacon is arranged below the frame for the guidance of the vehicle. Meanwhile, there is a red plate at the bottom of the acoustic beacon that helps the vehicle locate itself. The diameter of red plate is 400mm.
2.4.3 Instruction of Rules
The vehicle needs to emerge from the floating frame, which is basically fixed to a designated position on the surface of the water, to complete the task. Below the floating frame is an acoustic beacon set on a red disk, it can also be used as a means of vehicle cursor positioning.
It is judged to be a successful floating if the vehicle rises to float out of the frame and stays for more than 3 seconds. The vehicle gets full scores if it does not touch the frame, otherwise penalty points will be given.
2.5 End of Competition
After completing all the tasks, AUV floats onto the surface again outside the finish circle and applies for the end of the competition and the referee stops the countdown timer for 20 minutes. If all five tasks are scored, the remaining time is converted into "remaining time bonus".
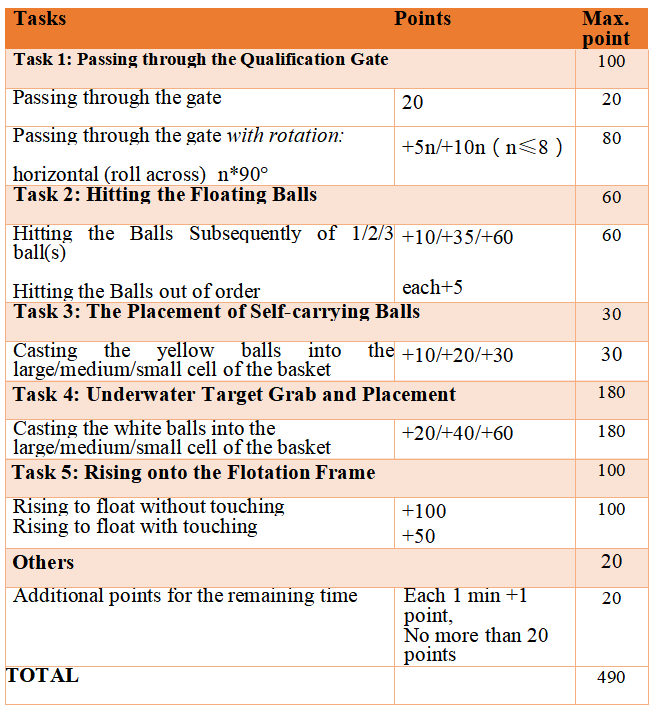
3.Scoring Rules
The total score is composed of work points completed within 20 minutes and remaining time bonus points, which can only be awarded if all tasks are completed within 20 minutes. The competition result is sorted according to the total score. If the scores are the same, the team with lower quality wins.
The above figures are for reference only, the competition is subject to the actual.
The organizing committee reserves the right of final interpretation.